Posts by Melinda Hamilton
Experts at Krull’s Composting
Learn all about Krull’s Composting in Northern Michigan. For more information on their services, check out their website: https://krullscomposting.com/ SHOW MORE
Read MoreSmart Gardens Begin with Healthy Soil
Cultivating a robust vegetable garden or a dazzling flower bed starts with healthy soil. Soils are a combination of different-sized mineral particles, organic matter and living organisms. The non-living or mineral part of the soil is made up of sand, silt and clay. Sand is the largest of the three particles and is big enough for…
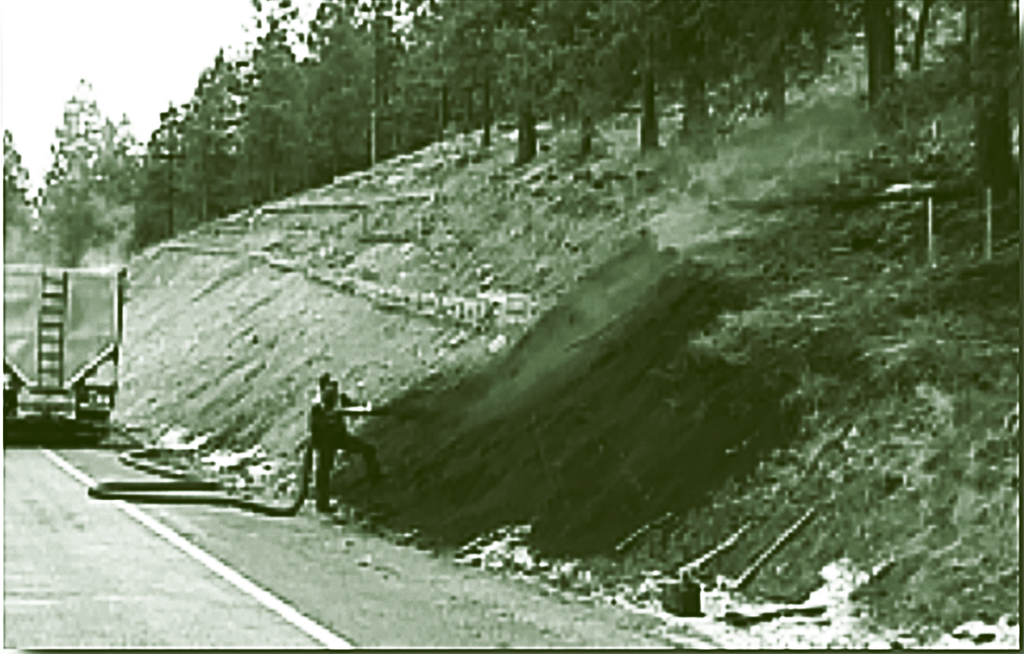
Read MoreCompost Use on State Highway Applications
CURRENT COMPOST USAGE BY STATE DOTS In order to determine the current usage of composted products by State DOTs, as well as their potential for increased usage, various information was gathered by surveying all 50 State DOTs. Once collected, this data was compiled into the following information sets: State DOT Compost Success Stories (case studies),…
Read MoreLearn How to Compost
When You Choose to Compost Your Waste, You Cultivate a Natural, Controlled Process That Converts Organic Minerals into Microorganisms. These are several benefits to consider: Recycle household waste Condition soil Support healthy soil Protect the environment Save money by reducing water loss Conserve natural resources Learn How to Compost Here
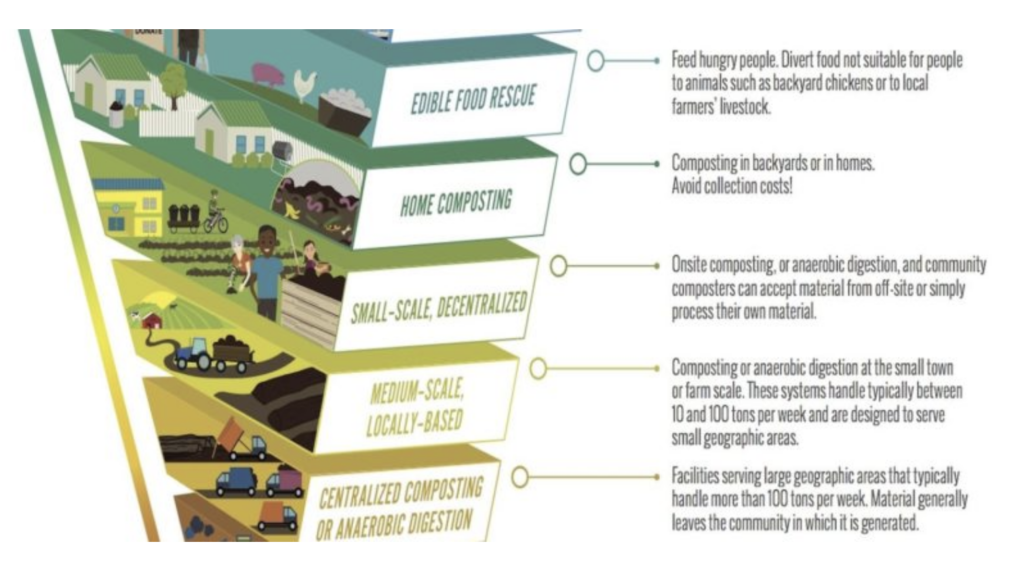
Read MoreHierarchy to Reduce Food Waste and Grow Community
Policy Tools for Capacity Building
The Waste to Wealth program seeks to encourage a composting infrastructure that is locally distributed and possesses a diversity of scales, feedstock materials, and end-uses for compost products. For more information, see ILSR’s report on “The State of Composting in the US” for a national snapshot of composting policy and models to replicate. State of Composting in the…
Read MorePerformance-Based Composting Permit Regulations
Performance-based compost regulations describe standards to be met without imposing restrictions on the exact way to meet those standards. Several states in the Pacific Northwest (such as Washington and Oregon), as well as Ohio in the Midwest have implemented performance-based standards, thereby acknowledging that no one regulatory model is best for every facility. These rules…
Read MoreOn-Farm Composting Rules and Permit Exemptions
Farmers have a vital role to play in producing and utilizing compost to restore depleted soils. Permit exemptions authorize compost operations on farms and smaller-scale facilities, such as community gardens, thus avoiding superfluous permitting requirements intended for larger, full-scale compost facilities. Because there are often significantly less risks or hazards associated with on-farm and small-scale composters,…
Read MoreFood Scrap Recovery Policies
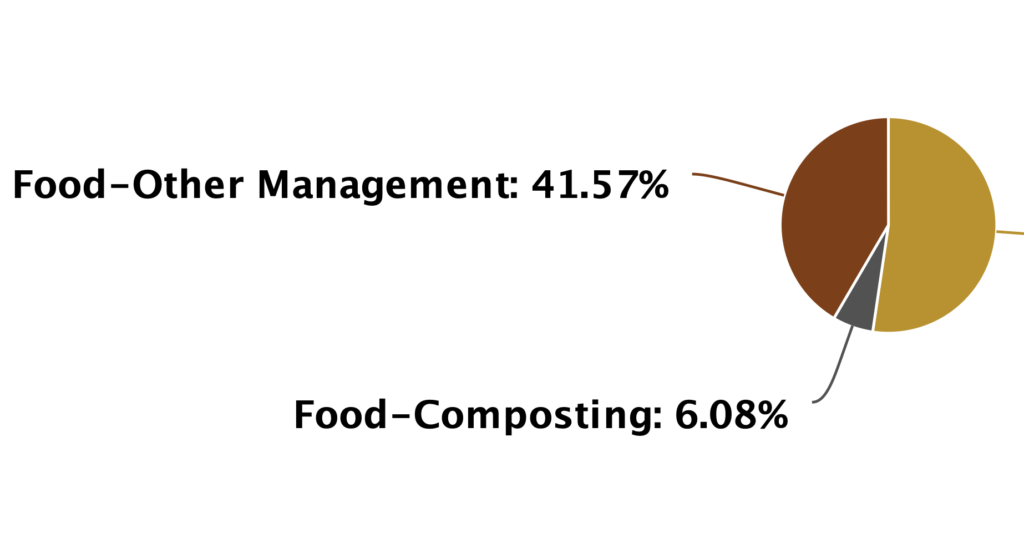
According to the US Environmental Protection Agency’s data on municipal solid waste generation and management, an estimated 52.4 percent of yard trimmings were “grasscycled” or composted in 2018, while only 6.1 percent of food scraps were composted. Policies that ban food scraps from landfills can have a tremendous and immediate effect on diverting organics from the…
Read MoreCompost -Amended Soil Requirements
Incorporating compost into soils that are disturbed or damaged by human development (such as typical construction practices) has many benefits for the overall health of the soil ecosystem including: improved water retention, increased infiltration rates, greater binding ability, pH stabilization, and micronutrient enrichment. These micro-level soil benefits in turn, lead to significant community benefits on…
Read More